- Svalbard
-
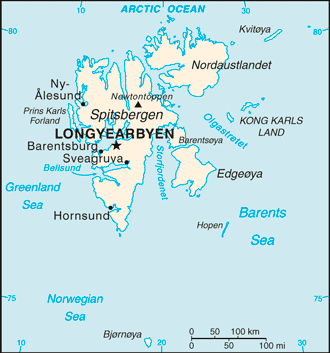 Introduction ::SvalbardBackground:First discovered by the Norwegians in the 12th century, the islands served as an international whaling base during the 17th and 18th centuries. Norway's sovereignty was recognized in 1920; five years later it officially took over the territory.Geography ::SvalbardLocation:Northern Europe, islands between the Arctic Ocean, Barents Sea, Greenland Sea, and Norwegian Sea, north of NorwayGeographic coordinates:78 00 N, 20 00 EArea:total: 62,045 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 125land: 62,045 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmnote: includes Spitsbergen and Bjornoya (Bear Island)Area - comparative:slightly smaller than West VirginiaLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:3,587 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 4 nmexclusive fishing zone: 200 nm unilaterally claimed by Norway but not recognized by RussiaClimate:arctic, tempered by warm North Atlantic Current; cool summers, cold winters; North Atlantic Current flows along west and north coasts of Spitsbergen, keeping water open and navigable most of the yearTerrain:wild, rugged mountains; much of high land ice covered; west coast clear of ice about one-half of the year; fjords along west and north coastsElevation extremes:lowest point: Arctic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Newtontoppen 1,717 mNatural resources:coal, iron ore, copper, zinc, phosphate, wildlife, fishLand use:arable land: 0%permanent crops: 0%other: 100% (no trees; the only bushes are crowberry and cloudberry) (2011)Irrigated land:NANatural hazards:ice floes often block the entrance to Bellsund (a transit point for coal export) on the west coast and occasionally make parts of the northeastern coast inaccessible to maritime trafficEnvironment - current issues:NAGeography - note:northernmost part of the Kingdom of Norway; consists of nine main islands; glaciers and snowfields cover 60% of the total area; Spitsbergen Island is the site of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault, a seed repository established by the Global Crop Diversity Trust and the Norwegian GovernmentPeople and Society ::SvalbardEthnic groups:Norwegian 55.4%, Russian and Ukrainian 44.3%, other 0.3% (1998)Languages:Norwegian, RussianPopulation:1,921 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 233Population growth rate:-0.03% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Sex ratio:NAInfant mortality rate:total: NAmale: NAfemale: NALife expectancy at birth:total population: NAmale: NAfemale: NATotal fertility rate:NAHIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0% (2001)country comparison to the world: 166HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:0 (2001)country comparison to the world: 163HIV/AIDS - deaths:0 (2001)country comparison to the world: 153Education expenditures:NALiteracy:NAGovernment ::SvalbardCountry name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Svalbard (sometimes referred to as Spitsbergen)Dependency status:territory of Norway; administered by the Polar Department of the Ministry of Justice, through a governor (sysselmann) residing in Longyearbyen, Spitsbergen; by treaty (9 February 1920) sovereignty was awarded to NorwayGovernment type:NACapital:name: Longyearbyengeographic coordinates: 78 13 N, 15 38 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in OctoberIndependence:none (territory of Norway)Legal system:the laws of Norway where applicable applyExecutive branch:chief of state: King HARALD V of Norway (since 17 January 1991)head of government: Governor Odd Olsen INGERO (since September 2009); Assistant Governor Lars Erik ALHEIMelections: none; the monarchy is hereditary; governor and assistant governor responsible to the Polar Department of the Ministry of JusticePolitical pressure groups and leaders:NAInternational organization participation:noneFlag description:the flag of Norway is usedNational anthem:note: as a territory of Norway, ""Ja, vi elsker dette landet"" is official (see Norway)Economy ::SvalbardEconomy - overview:Coal mining, tourism, and international research are the major revenue sources on Svalbard. Coal mining is the dominant economic activity and a treaty of 9 February 1920 gave the 41 signatories equal rights to exploit mineral deposits, subject to Norwegian regulation. Although US, UK, Dutch, and Swedish coal companies have mined in the past, the only companies still engaging in this are Norwegian and Russian. The settlements on Svalbard are essentially company towns. The Norwegian state-owned coal company employs nearly 60% of the Norwegian population on the island, runs many of the local services, and provides most of the local infrastructure. There is also some hunting of seal, reindeer, and fox. Goods such as alcohol, tobacco, and vehicles, normally highly taxed on mainland Norway, are considerably cheaper in Svalbard in an effort by the Norwegian government to entice more people to live on the Arctic archipelago. By law, the Norwegians collect only enough taxes to pay for the needs of the local government; none of tax proceeds go to Norway.GDP (purchasing power parity):$6.313 billionGDP - real growth rate:NA%Labor force:1,234 (2003)country comparison to the world: 229Budget:revenues: $NAexpenditures: $NATaxes and other revenues:NA% of GDPBudget surplus (+) or deficit (-):NA% of GDPExports:$NAImports:$NAExchange rates:Norwegian kroner (NOK) per US dollar -5.8162 (2012)5.6065 (2011)6.0442 (2010)6.288 (2009)5.6361 (2008)Communications ::SvalbardTelephone system:general assessment: adequatedomestic: local telephone serviceinternational: country code - 47-790; satellite earth station - 1 of unknown type (for communication with Norwegian mainland only) (2005)Broadcast media:the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation (NRK) began direct TV transmission to Svalbard via satellite in 1984; Longyearbyen households have access to 3 NRK radio and 2 TV stations (2008)Internet country code:.sjTransportation ::SvalbardAirports:4 (2013)country comparison to the world: 188Airports - with paved runways:total: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 3under 914 m:3 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Ports and terminals:Barentsburg, Longyearbyen, Ny-Alesund, PyramidenMilitary ::SvalbardMilitary branches:no regular military forcesMilitary - note:Svalbard is a territory of Norway, demilitarized by treaty on 9 February 1920; Norwegian military activity is limited to fisheries surveillance by the Norwegian Coast GuardTransnational Issues ::SvalbardDisputes - international:despite recent discussions, Russia and Norway dispute their maritime limits in the Barents Sea and Russia's fishing rights beyond Svalbard's territorial limits within the Svalbard Treaty zone"
Introduction ::SvalbardBackground:First discovered by the Norwegians in the 12th century, the islands served as an international whaling base during the 17th and 18th centuries. Norway's sovereignty was recognized in 1920; five years later it officially took over the territory.Geography ::SvalbardLocation:Northern Europe, islands between the Arctic Ocean, Barents Sea, Greenland Sea, and Norwegian Sea, north of NorwayGeographic coordinates:78 00 N, 20 00 EArea:total: 62,045 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 125land: 62,045 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmnote: includes Spitsbergen and Bjornoya (Bear Island)Area - comparative:slightly smaller than West VirginiaLand boundaries:0 kmCoastline:3,587 kmMaritime claims:territorial sea: 4 nmexclusive fishing zone: 200 nm unilaterally claimed by Norway but not recognized by RussiaClimate:arctic, tempered by warm North Atlantic Current; cool summers, cold winters; North Atlantic Current flows along west and north coasts of Spitsbergen, keeping water open and navigable most of the yearTerrain:wild, rugged mountains; much of high land ice covered; west coast clear of ice about one-half of the year; fjords along west and north coastsElevation extremes:lowest point: Arctic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Newtontoppen 1,717 mNatural resources:coal, iron ore, copper, zinc, phosphate, wildlife, fishLand use:arable land: 0%permanent crops: 0%other: 100% (no trees; the only bushes are crowberry and cloudberry) (2011)Irrigated land:NANatural hazards:ice floes often block the entrance to Bellsund (a transit point for coal export) on the west coast and occasionally make parts of the northeastern coast inaccessible to maritime trafficEnvironment - current issues:NAGeography - note:northernmost part of the Kingdom of Norway; consists of nine main islands; glaciers and snowfields cover 60% of the total area; Spitsbergen Island is the site of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault, a seed repository established by the Global Crop Diversity Trust and the Norwegian GovernmentPeople and Society ::SvalbardEthnic groups:Norwegian 55.4%, Russian and Ukrainian 44.3%, other 0.3% (1998)Languages:Norwegian, RussianPopulation:1,921 (July 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 233Population growth rate:-0.03% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 200Sex ratio:NAInfant mortality rate:total: NAmale: NAfemale: NALife expectancy at birth:total population: NAmale: NAfemale: NATotal fertility rate:NAHIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate:0% (2001)country comparison to the world: 166HIV/AIDS - people living with HIV/AIDS:0 (2001)country comparison to the world: 163HIV/AIDS - deaths:0 (2001)country comparison to the world: 153Education expenditures:NALiteracy:NAGovernment ::SvalbardCountry name:conventional long form: noneconventional short form: Svalbard (sometimes referred to as Spitsbergen)Dependency status:territory of Norway; administered by the Polar Department of the Ministry of Justice, through a governor (sysselmann) residing in Longyearbyen, Spitsbergen; by treaty (9 February 1920) sovereignty was awarded to NorwayGovernment type:NACapital:name: Longyearbyengeographic coordinates: 78 13 N, 15 38 Etime difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC during Standard Time)daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in OctoberIndependence:none (territory of Norway)Legal system:the laws of Norway where applicable applyExecutive branch:chief of state: King HARALD V of Norway (since 17 January 1991)head of government: Governor Odd Olsen INGERO (since September 2009); Assistant Governor Lars Erik ALHEIMelections: none; the monarchy is hereditary; governor and assistant governor responsible to the Polar Department of the Ministry of JusticePolitical pressure groups and leaders:NAInternational organization participation:noneFlag description:the flag of Norway is usedNational anthem:note: as a territory of Norway, ""Ja, vi elsker dette landet"" is official (see Norway)Economy ::SvalbardEconomy - overview:Coal mining, tourism, and international research are the major revenue sources on Svalbard. Coal mining is the dominant economic activity and a treaty of 9 February 1920 gave the 41 signatories equal rights to exploit mineral deposits, subject to Norwegian regulation. Although US, UK, Dutch, and Swedish coal companies have mined in the past, the only companies still engaging in this are Norwegian and Russian. The settlements on Svalbard are essentially company towns. The Norwegian state-owned coal company employs nearly 60% of the Norwegian population on the island, runs many of the local services, and provides most of the local infrastructure. There is also some hunting of seal, reindeer, and fox. Goods such as alcohol, tobacco, and vehicles, normally highly taxed on mainland Norway, are considerably cheaper in Svalbard in an effort by the Norwegian government to entice more people to live on the Arctic archipelago. By law, the Norwegians collect only enough taxes to pay for the needs of the local government; none of tax proceeds go to Norway.GDP (purchasing power parity):$6.313 billionGDP - real growth rate:NA%Labor force:1,234 (2003)country comparison to the world: 229Budget:revenues: $NAexpenditures: $NATaxes and other revenues:NA% of GDPBudget surplus (+) or deficit (-):NA% of GDPExports:$NAImports:$NAExchange rates:Norwegian kroner (NOK) per US dollar -5.8162 (2012)5.6065 (2011)6.0442 (2010)6.288 (2009)5.6361 (2008)Communications ::SvalbardTelephone system:general assessment: adequatedomestic: local telephone serviceinternational: country code - 47-790; satellite earth station - 1 of unknown type (for communication with Norwegian mainland only) (2005)Broadcast media:the Norwegian Broadcasting Corporation (NRK) began direct TV transmission to Svalbard via satellite in 1984; Longyearbyen households have access to 3 NRK radio and 2 TV stations (2008)Internet country code:.sjTransportation ::SvalbardAirports:4 (2013)country comparison to the world: 188Airports - with paved runways:total: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 1 (2013)Airports - with unpaved runways:total: 3under 914 m:3 (2013)Heliports:1 (2013)Ports and terminals:Barentsburg, Longyearbyen, Ny-Alesund, PyramidenMilitary ::SvalbardMilitary branches:no regular military forcesMilitary - note:Svalbard is a territory of Norway, demilitarized by treaty on 9 February 1920; Norwegian military activity is limited to fisheries surveillance by the Norwegian Coast GuardTransnational Issues ::SvalbardDisputes - international:despite recent discussions, Russia and Norway dispute their maritime limits in the Barents Sea and Russia's fishing rights beyond Svalbard's territorial limits within the Svalbard Treaty zone"
The World Factbook. 2014.
